What is Wheat?
Wheat is one of the most consumed cereals in the world. It comes from a variety of herbs (Triticum) grown in countless types around the world. Soft Wheat, or soft Wheat, is the primary type. Several other closely related species include durum wheat, einkorn, and Khorasan wheat.
White and wholemeal flours are fundamental ingredients in baked goods such as bread. Other wheat-based foods include noodles, noodles, semolina, bulgur, and couscous. Basically, it is a considerable controversy because it contains gluten, triggering a harmful immune response in susceptible people.
However, whole wheat can be a rich source of various antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and fibre for people who tolerate it.
The Nutritional Value
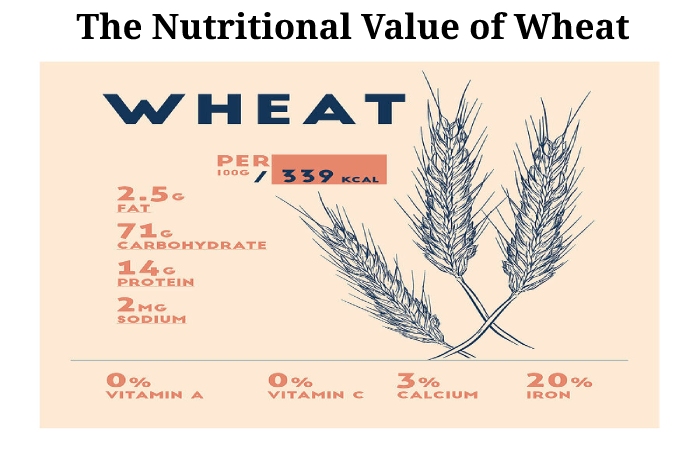
Wheat is mainly composed of carbohydrates, but it also contains a moderate amount of protein.
Here is the nutritional value per 100 grams of whole wheat flour (1):
Calories: 340
Water: 11%
Protein: 13.2 grams
Carbohydrates: 72 grams
Sugar: 0.4 grams
Fibre: 10.7 grams
Fat: 2.5 grams
1. Carbohydrates
Like all grains, it is mainly composed of carbohydrates. Starch is the predominant carbohydrate in the plant kingdom, accounting for over 90% of its total carbohydrate content.
Basically, the health effects of starch depend primarily on its digestibility, which determines its impact on blood sugar levels.
However, high digestibility can cause unhealthy blood sugar spikes after meals and harm health, especially in people with diabetes.
2. Fiber
Whole wheat is very high in fibre, but refined is almost free. It has a fibre content of 12-15% on the dry weight. Basically, most of its fibre is insoluble, passes through the digestive system almost unchanged, and increases stool volume. Some fibres also feed intestinal bacteria.
Additionally, it contains small amounts of soluble fibre or fructans, which can cause digestive symptoms in people with irritable bowel syndrome.
3. Proteins
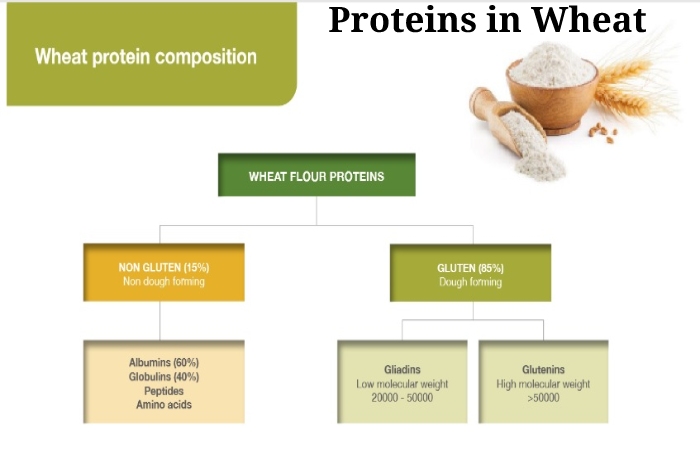
Protein makes up 7-22% of the dry weight of it (1, 10) Gluten, a massive family of proteins, accounts for up to 80% of total protein. Moreover, it is responsible for the unique elasticity and viscosity of its dough – properties that make it so beneficial for bread baking.
However, wheat gluten canisters have adverse health effects in people with Gluten Intolerance.
Vitamins And Minerals
Whole wheat is a moral source of several vitamins and minerals. As with most cereals, the amount of minerals depends on the soil in which they are grown.
1. Selenius:
This trace mineral has various vital functions in the body. The selenium content of it must be contingent on the soil and is very low in some regions, including China.
2. Manganese:
High in whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, manganese can be poorly absorbed from whole wheat due to its phytic acid content.
3. Phosphorus:
This dietary mineral plays an essential role in maintaining and growing body tissues.
4. Copper:
An essential trace mineral, copper, is often found in low-content Western diets. A deficiency can have negative consequences for heart health.
5. Folic Acid:
One of the B vitamins, folic acid, is also known as folate or vitamin B9. It is crucial during pregnancy.
Fortified flour can be a good source of iron, thiamine, niacin, calcium, and vitamin B6, in addition to the nutrients mentioned above.
Health Benefits Of Whole Wheat
White wheat may not be beneficial to health and it can have several beneficial effects, especially when it replaces white flour.
1. Gut Health

Whole wheat is rich in insoluble fibre, which is concentrated in the bran. Research suggests that components in its bran may act as prebiotics, feeding some beneficial bacteria in the gut (8).
2. Colon Cancer Prevention
Colon cancer is the most common type of digestive cancer.
Observational studies have linked the consumption of whole grains, including whole grains, to a reduced risk of colon cancer.
In general, whole wheat is high in fibre and contains several antioxidants and phytonutrients that can reduce the risk of colon cancer.
Other Disadvantages And Side Effects
While whole wheat may have some health benefits, many people need to eat less or avoid it altogether.
1. Sensitivity To Wheat
The number of people on a gluten-free diet exceeds the number of people with celiac disease. Sometimes people think that wheat and gluten are inherently unhealthy. In other cases, wheat or gluten can cause genuine symptoms.
This condition, called gluten sensitivity or gluten-free sensitivity, is an adverse reaction to it with no autoimmune or allergic reactions.
2. IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
IBS is a mutual condition characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, irregular bowel movements, diarrhoea, and constipation.
It is more common in people suffering from anxiety and is often triggered by a stressful life event (50). Wheat sensitivity is common among people with IBS.
3. Allergy
Food allergy is a common condition in which harmful immune response to specific proteins. Gluten in wheat is a significant allergen, affecting approximately 1% of children. In adults, allergies most often occur in those who regularly come into contact with airborne dust.
Baker’s asthma and nasal inflammation are typically allergic reactions to its dust.
Conclusion
Wheat is one of the most common foods in the world and one of the most controversial. People with gluten intolerance should eliminate it from their diet.
Also Read: Cherries – Health Benefits, Ways to incorporate cherries into your diet, Even could kill you
Related searches:
[wheat origin]
[wheat meaning]
[wheat nutrition]
[wheat flour]
[wheat scientific name]
[wheat crop]
[wheat definition]
[wheat seeds]


