Turnip
Turnip, also known as white turnip, is a hardy biennial plant of the mustard family (Brassicaceae), cultivated for its fleshy roots tender tops. It is believed that the turnip originated in Central and East Asia and is produced in the temperate zone.
Young turnip roots are eaten raw or pickled in salads, while young leaves can be cooked and served. The seeds are also boiled and done whole or mashed and used in stews. Although they are sometimes called yellow or waxy turnips, kohlrabi (Brassica napus, a variety of Napobrassika) is an, unlike species.
The turnip root is shaped by the thickening of the seedling’s taproot and the base of the young stem directly above it. The branch stays short for the first year and has leaves that form a rose at the top of the root.
Turnip Nutrition
Turnip has an excellent nutritional profile. Like other cruciferous vegetables, they are low in calories but high in vitamins and minerals.
1 cup (130 grams) diced raw turnips contains:
Calories: 36
Carbohydrates: 8 grams
Fibre: 2 grams
Protein: 1 gram
Vitamin C: 30% Daily Value (DV)
Folic acid: 5% of the DV.
Phosphorus: 3% DV
Calcium: 3% of the DV
Turnip Greens Nutrition
Turnip Greens contain even more nutrients, such as 1 cup (55 grams) of chopped turnip greens.
Calories: 18
Carbohydrates: 4 grams
Fibre: 2 grams
Vitamin K: 115% of the RDI
Vitamin C: 37% of the RDI.
Provitamin A: 35% of the daily value.
Folic acid: 27% of the DV.
Calcium: 8% of the RDI
What Are The Benefits Of Turnips?
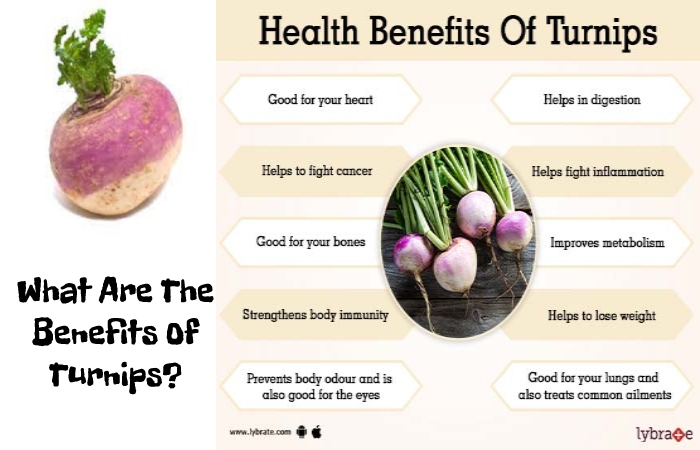
Many researchers and health professionals have faith that the nutrients in turnip have a wide range of health benefits, such as:
1. Eliminate Intestinal Problems
One cup of raw turnips weighing 130 grams (g) provides 2.34 grams of fibre. Fibre helps decrease pressure and inflammation in the colon.
In particular, a high-fibre diet is associated with a lower risk of intestinal problems, including diverticulitis.
Turnips and other high-fibre foods can help reduce the frequency of diverticulitis flare-ups by absorbing water in the colon and facilitating bowel movements. However, doctors don’t always recommend a high-fibre diet for people with diverticulitis. Talk to your doctor before eating high-fibre foods.
2. Low Blood Pressure
Foods that contain nitrates in the diet, such as turnips and kale greens, can have many benefits for blood vessel health. These include lowering blood pressure and inhibiting the build-up of platelets in the blood.
However, the long-term risks of a diet rich in nitrates and its effects on cardiovascular health remain unclear.
Turnip also contains potassium, which can help lower blood pressure by releasing sodium from the body and helping arteries dilate.
3. Reduce The Risk of Cancer
A high intake of cruciferous vegetables, including turnips, cauliflower, and cabbage, has been linked to lower cancer risk. These vegetables contain several compounds that can have protective effects against certain types of cancer.
Foods containing a compound called sulforaphane also can play an essential role in treating cancer. Cruciferous vegetables contain high levels of sulforaphane.
4. Promotes Weight Loss and Digestion
Turnip and other high-fibre cruciferous vegetables help people feel fuller longer and are low in calories. Eating foods high in fibre also helps keep blood sugar levels stable.
The fibre in turnips can also prevent constipation and promote regular digestive health. Normal and proper bowel movements are essential for the elimination of toxins in the bile and stool.
Both their roots and leaves, also known as turnip greens, are safe to eat. And like most cruciferous vegetables, they have health-promoting effects.
Both the roots and leaves are excellent sources of vitamin C, which protects your body from free radical damage when levels of these molecules in the body become too high.
More Health Benefits Of Turnip
Turnip belongs to the Brassica family, which includes kale, broccoli, kale, and Brussels sprouts. It is a tuber native to Europe and grows well at lower temperatures. Small, tender turnip varieties are the most common on the menu, as they are less bitter and healthier than the larger varieties.
Like all vegetables, turnips are very low in saturated fat and cholesterol. They are a good source of vitamin B6, folate, calcium, potassium, and copper. An excellent basis of dietary fibre, vitamin C, and manganese.
Turnip greens are a nutrient-dense superfood. They are a good source of protein, thiamine, riboflavin, pantothenic acid, iron, and phosphorus. Turnip greens are an excellent source of dietary fibre, vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin K, vitamin B6, folate, calcium, magnesium, potassium, copper, and manganese.
The turnip goes well with cream and coconut milk; coriander, nutmeg, turmeric, parsley, or thyme; fried and stewed bacon or meat; salty cheeses like Parmesan; other root vegetables or mushrooms; honey, sherry, or lemon.
Related searches:
[turnip in telugu]
[turnip in hindi]
[turnip vs radish]
[turnip meaning]
[turnip company]
[turnip app]
[turnip recipes]
[turnip pronunciation]


