Saline Types: Fluids for IV Administration
Chronic or acute dehydration, both states require drip therapy to fix. Drinking a few gallons of water would just deteriorate water-salt balance, causing harm to the body, so best medicine and wellness practices recommend going with IV hydration treatments in the first place.
IV drips are blood-compatible liquids in which some essential nutrients (vitamins, minerals, amino acids) are mixed in saline — solvent. Let’s learn more about saline solutions.
What Is Saline in Drip Therapy and Why It’s that Vital?
Every living cell has its own cellular metabolism. It’s essential for the transport of nutrients, regulation of body temperature, joint lubrication, elimination of waste, shock absorption, and more. But, for some reason, the electrolyte-water balance may become imbalanced, causing stress to body systems. Basically, it leads to cognitive function impairment, blood concentration, inadequate blood pressure, and more.
Saline is the blood-compatible solution which is basically the optimal match of electrolyte (NaCl, or simply salt) in water for injection. It’s a crystalloid solution, meaning it contains particles moving freely from the bloodstream to cells. There are three types of crystalloids ranking based on their ability to make water move into or out of cells.
- Hypotonic solution (lower osmolarity than in cells).
- Hypertonic (higher osmolarity than in cells).
- Isotonic (same osmolarity as in cells).
By choosing an appropriate solution, it’s possible to administer the fluid that would match the state of cells and normalize their internal water-salt balance.
Also Read: 10 Different Common Causes of Chest Pain
What Are the Types of Normal Saline and How to Choose a One?
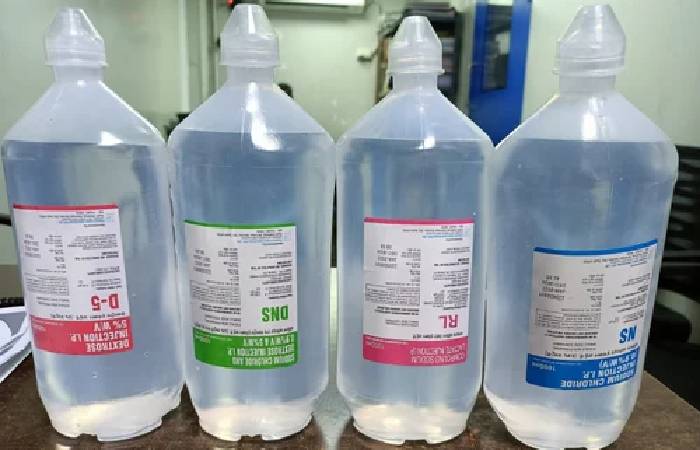

There are four types of saline in use:
- Normal saline — 0.9% of NaCl in water.
- Half-normal saline — 0.45% of NaCl in water.
- Lactate ringers (similar to blood plasma).
- Dextrose — 5% of dextrose sugar in water.
you should understand that in conventional medicine, healthcare providers select appropriate saline themselves when it comes to urgent help. Lactate ringers and dextrose are specific types of saline normally used when a patient is injured and loses a significant amount of blood or suffers from malnutrition in addition to dehydration, etc.
Half normal saline (hypotonic) is more for cases of acute dehydration accompanied by poor water-salt balance. Typically, IV drip administrations that you may request are all normal saline-based (isotonic), which is fine.