What is Bloodwork?
Bloodwork is a regular blood test and is one of the most important ways to monitor your overall physical well-being. Regular tests can allow you to see how your body changes over time and enable you to make informed decisions about your health.
Blood tests are laboratory tests performed to control blood after blood from a vein using an individual needle. These tests measure each biochemical substance found in the body to diagnose any disease’s presence.

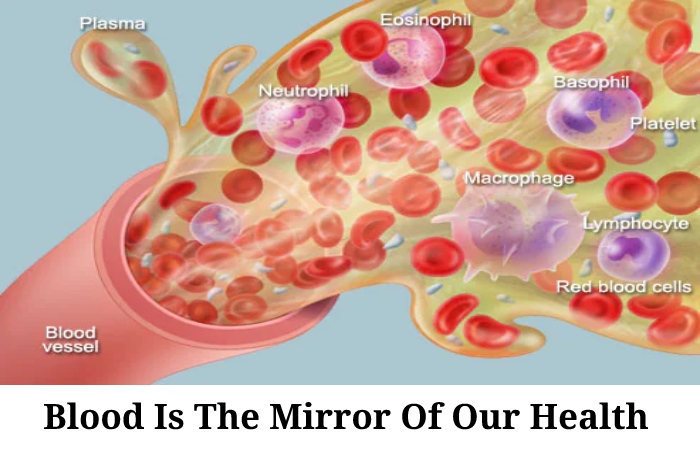
Blood Is The Mirror Of Our Health
And, despite being a liquid, it is one more tissue of our body. A tissue allows all body organs to receive the nutrients and oxygen necessary for their metabolism while collecting waste substances for disposal from the body.
In other words, blood is that liquid medium that allows the organs and tissues of the body to stay alive. Through it, blood cells flow red blood cells (99% of all) for the transport of oxygen, white blood cells for the immune system’s functionality, and platelets for blood clotting.
But it’s not just the blood cell highway. Hormones also flow through the blood, which travels through it until they reach the organs where they have to act, and minerals, vitamins, nutrients, and all the substances that, in one way or another, determine our health, including possible pathogens.
Therefore, a blood test is a clinical procedure in which the pathologist studies a person’s blood composition. Extraction of blood using a syringe is necessary, which collects blood from a vein in the arm. It is usually done in the veins, although it can also be done with arterial blood.
In short, a blood test is a laboratory diagnostic technique that, through chemical analysis of the blood, allows us to obtain information about the general state of health and detector. If there are already suspicions, confirm or reject different diseases that manifest themselves with an alteration in the blood composition.
Types Of Blood Tests (Bloodwork)
There are general blood tests and more specific blood tests, which can cost quite a bit of money. Such tests are DNA tests, tests for the control of gene abnormalities, and viral analyses.
The blood tests usually carried out are as follows: general blood, vitamin B12 control, ferritin control, folic acid, Coobs zero reaction, hemoglobin electrophoresis, iron, red sedimentation speed, flow-coagulation time, prothrombin time.
Blood tests, in general, have the following categories:
- Haematological (control of the hemodynamic function of the bone marrow)
- Biochemicals (control of trace elements, enzymes, and other substances involved in metabolism)
- Hormonal (control of hormones produced by the endocrine glands)
- Neoplasia indicators (control of substances produced by neoplastic cells in large quantities)
- Molecular analyses (control of DNA mutations, paternity, viruses, and parasites)
- Toxicological tests (testing of toxic substances and elements found in the body)
- Immunological (control of infections, autoimmune diseases, vaccinations
How Are Blood Tests (Bloodwork) Carried Out?
To do the blood test, blood collection by a qualified doctor is necessary.
Venous catheterization is a helpful method of blood isolation to isolate cells and extracellular fluid from the body for laboratory testing.
The blood taken is checked in special laboratories, and the findings are given in written form to the patient.
Preparation Of Blood Tests (Bloodwork)
Blood tests are mostly done in the morning hours. The results are not affected by breakfast, except for tests concerning metabolism (sugar, triglycerides, cholesterol). The latter requires overnight fasting of 12 hours.
Biochemical blood tests require 12-hour fasting. Water doesn’t affect the tests.
Hormonal examinations do not require any fasting or other preparation.
For drug-level tests, blood tests are primarily carried out in the morning and before taking the relevant medicine.
Examinations of neoplastic markers do not require fasting, and blood can be collected at any time of the day.
For thyroid tests, thyroid medication should be taken after blood collection.
How Long Does Bloodwork Take To Get The Result?
It may take from some hours to some days to get results. Here’s an overview of the duration of some of the standard tests:
- Complete blood count: 24 hours
- Basic metabolic panel: 24 hours
- Complete metabolic panel: 24-72 hours
- Lipid panel: 24 hours.
Sometimes the lab will only share the results with your doctor, who will review them and then provide you with them.
What Types Of Blood Tests Are There?
There are many different types of blood tests. And, in addition to the three main types of blood cells, in the blood, there are hundreds of other chemicals, hormones, and minerals, as well as nutrients, proteins, lipids, fats (the famous cholesterol), and all kinds of metabolic products.
Therefore, there could be a type of analysis for each of these substances. Anyway, in today’s article, we have collected the most common ones: the ones most frequently used in the day-to-day clinic to prevent and diagnose diseases or check the general health status. Below we see the most commonly used blood tests.
1. Complete Blood Count (CBC)
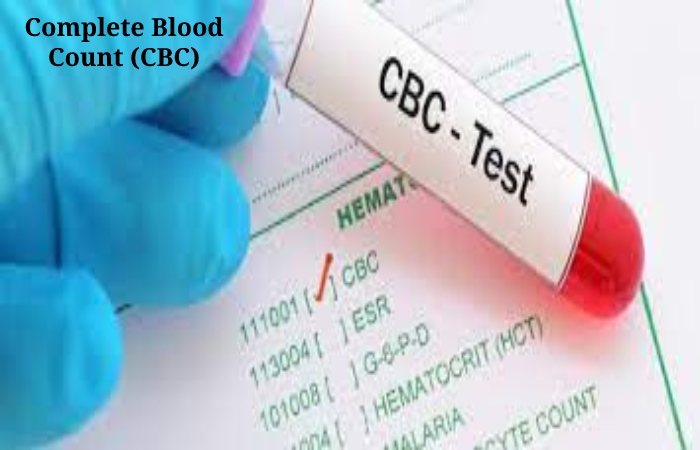
The complete blood count or hematology is the most common blood test performed in routine medical check-ups to analyze the general health status.
A routine complete blood count (CBC) test checks for levels of 10 different components of every primary cell in your blood: white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. Important features measured by this test include red blood cell count, hemoglobin, and hematocrit.
Here’s the typical range of results:
| Component | Normal range |
| red blood cells | men: 4.32–5.72 million cells/mcL; women: 3.90–5.03 million cells/mcL |
| white blood cells | 3,500 to 10,500 cells/mcL |
| platelets | 150,000 to 450,000/mcL |
| hemoglobin | men: 13.5–17.5 grams/deciliter (g/dL); women: 12.0–15.5 g/dL |
| hematocrit | men: 38.8–50.0 percent; women: 34.9–44.5 percent |
2. Coagulation Test
A clotting test is a blood test performed when problems in platelet levels are seen after a complete blood count. Therefore, it is necessary to do this test to measure the blood clotting capacity, whether it is too high (risk of thrombi or clots) or too low (risk of bleeding).
3. Thyroid Profile
The thyroid gland is an essential part of the endocrine system because it synthesizes and releases hormones like thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
These hormones regulate the rate at which metabolic processes occur throughout the body, having countless functions in the body.
4. Lipid Profile
Controlling lipid levels, especially cholesterol and triglycerides, is of utmost importance in people who suffer from cardiovascular disease (the most evident example is hypercholesterolemia)or are at risk of developing one. Fats are not bad, but they can build up and form a plaque that clogs the blood vessels when they are in excess.
5. Iron Profile
Iron is an essential mineral to form red blood cells. And, both by not including foods rich in it in the diet and by problems in its absorption, it may be that the person presents an iron deficiency, which can lead to anemia. This type of blood test measures iron levels in people who have symptoms of pallor, weakness, abdominal swelling, fatigue, etc., all of which are typical of the lack of this mineral.
6. Vitamin D Analysis
Vitamin D deficiency is one of the most common vitamin deficiencies globally. It can develop in people who do not sunbathe enough and who follow diets deficient in this vitamin.
Conclusion
(Bloodwork) Blood tests provide a meaningful picture of your overall health. They are also an excellent way to detect a disease or ailment early or check how well your body responds to treatments for various diseases.
Get repetitive blood tests at least once a year. Talk to your doctor to see any other tests you may need to ensure optimal health.
Also Read: Omega-3 – Side-Effects, Benefits of Omega-3, Fish Oil for Heart Disease
Related Searches:
[bloodwork meaning]
[bloodwork movie]
[is bloodwork one word]
[bloodwork results]
[bloodwork labs]
[bloodwork cbc]
[bloodwork or blood work]
[bloodwork spelling]


